Process of Conception
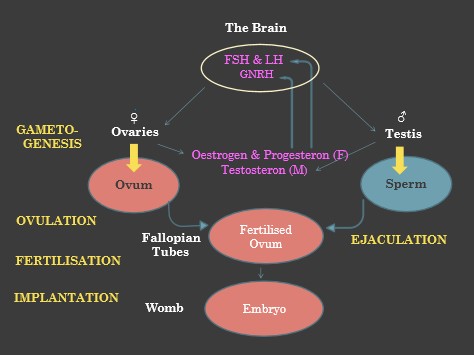
The process of conception starts in the brain. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland secrete hormones that stimulate the function of the reproductive organs. This is regulated through a negative feedback system, constantly adjusting the system to meet the hormonal requirements needed at different circumstances.
The Stages of Conception
- Gametogenesis; The production / ripening of the gametes; eggs and sperm.
- Releasing of the eggs or sperm; ovulation & ejaculation resp
- Fertilization of the egg by a single sperm cell
- Implantation of the embryo in the womb.
A woman releases only one egg every month. After it breaks free Released from the ovary, the egg cell is caught by the fimbriae (the brush like end of the fallopian tube) where hair-like cells transport it down towards the womb.
The testis of a man continuously produces sperm cells. In every ejaculate he releases millions of sperm cells. When sperms are laid in the vagina they actively swim up into the cervical canal, up into the womb and on into the fallopian tubes. Only one fast fit sperm cell will be able to penetrate the egg. Still in the fallopian tube, the male and female cell cores fuse and fertilization is fact, forming a unique human genome.
The fertilized egg divides in 2, 4, 8 cells etc, at the same time slowly descents to the womb. After about one week the embryo, by then some 100 cells, will have reached the womb and implants.
What can cause infertility?

The reproductive hormonal balance is influenced by many factors and can easily be disturbed. In the hierarchy of body functions, reproduction ranks low. In case of any major stress (physical or emotional), pregnancy may be contra-indicated and other, more vital functions will be given priority.
Anatomical abnormalities can disrupt the transport of gametes or interfere with implantation. Conditions in the womb or the vascular system may disturb development & grows of the embryo.
Causes of Male Infertility
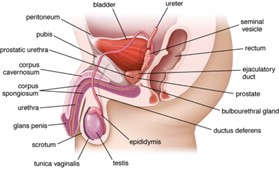
- Spermatomatogenesis:
- Hormonal: Hyperlipidaemia, DM, etc
- Chemical: Drugs, Toxics…
- Congenital: Chromosonal abnormalities
- Anatomical: Varicocele, Trauma, Infections
- Transportation of Sperm: Prostate enlargement, Infections (STD’s, TB)
- Ejaculation: Hormonal, Anatomical, Vascular or Nerve Damage, Intoxications or Stress!
Causes of Female Infertility
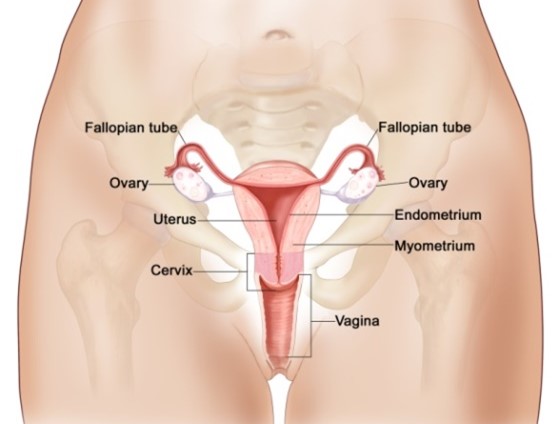
- Ovulation:
- PCOS, POF, Hyperprolactinaemia, Thyroid, Hyperlipidaemia, Obesity, Anorexia, Stress!
- Fallopian Tube Damage:
- Infections! STD’s, FGM, Unsafe Abortions
- Scar Tissue (Trauma / Surgery), Endometriosis
- Structural Abnormalities of the Womb Fibroid, Congenital Malformations
- Miscellaneous: Vaginal Douches / Tobacco
Go back to Infertility